Transoral robotic surgery (TORS) has emerged as a groundbreaking approach in the realm of surgical oncology, especially for conditions affecting the head and neck. This minimally invasive technique leverages advanced robotic technology to perform complex procedures, offering advantages that traditional surgical methods may lack. With its increasing application in treating tumors and various medical conditions, TORS represents not just a technological innovation but also a significant shift in surgical philosophy.
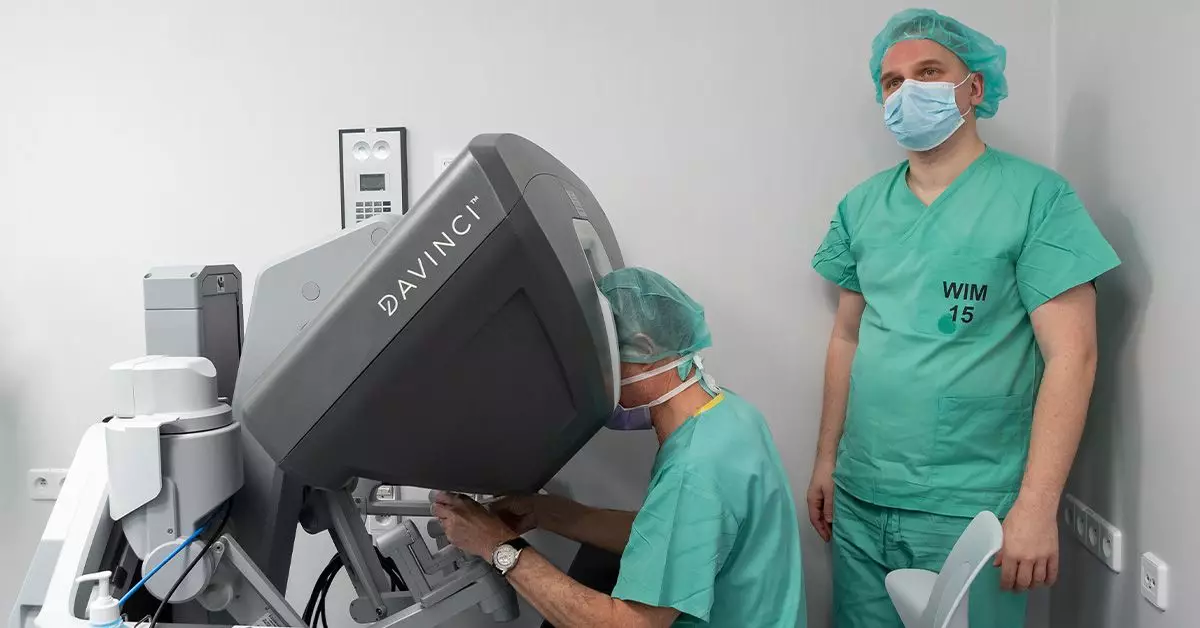
At its core, TORS involves the use of the Da Vinci Surgical System (DVSS), an intricate robotic apparatus designed to facilitate precise surgical maneuvers within the limited visibility and access that the oral cavity presents. Unlike traditional approaches that often require significant external incisions, TORS is conducted transorally, meaning all operations are performed through the mouth. This not only minimizes trauma to surrounding tissues but also enhances post-operative recovery experiences.
The DVSS itself is equipped with articulated robotic arms, which reproduce the delicate movements of a surgeon’s hands but with an increased range of motion. The central arm houses a high-resolution camera that provides surgeons with a magnified and detailed view of the surgical field, while the side arms function as instrumental extensions for various surgical tasks. Surgeons manipulate these robotic arms from a console, allowing for precision and control that can surpass conventional techniques.
Benefits Over Traditional Surgical Techniques
The benefits of TORS extend beyond mere aesthetics. Research indicates that procedures performed using this technique are associated with shorter hospital stays and quicker recovery times compared to traditional surgical methods. Additionally, patients experience reduced postoperative complications, such as infections or excessive scarring, since external incisions are largely eliminated. A review from 2022 corroborated that TORS also enabled more efficient thyroid surgeries and neck dissections, showcasing its versatility across various head and neck disorders.
Furthermore, the feasibility of TORS as a dual-purpose approach has gained traction. A 2023 study highlighted its effectiveness not only in treating but also in diagnosing squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) by helping surgeons accurately identify primary tumors. Accurate tumor identification is crucial, as it hinges on the formulation of effective cancer treatment strategies and enhances the likelihood of successful outcomes.
The Ongoing Evolution of Robotic Surgery
Despite its myriad advantages, the advancement of TORS is not without challenges and limitations. As with any robotic system, there exists a risk for mechanical failures, although the probability is relatively low at approximately 0.1% to 0.5%. Additionally, the success of TORS is tied closely to the proficiency of the surgical team; centers that perform a higher volume of TORS procedures tend to report significantly better patient outcomes. This suggests that experience and specialization play critical roles in the efficacy of robotic surgery.
Moreover, while TORS may provide surgeons with improved dexterity, the technique demands rigorous training and an understanding of robotic systems, marking a departure from traditional surgical training paradigms. As robotic surgery gains popularity, ongoing education and adaptation within surgical communities will be essential to harness its full potential.
Following TORS, patient recovery is typically more expedient than with conventional surgeries. While every individual’s healing process varies based on their overall health and the extent of the operation, most patients can anticipate a return to a normal diet within days, starting with liquids and progressing to soft foods. The role of speech and swallowing specialists often proves vital during this transition, ensuring that patients adjust well post-surgery.
Long-term follow-up is another critical dimension of TORS, particularly for oncology patients. Regular monitoring for signs of cancer recurrence remains a fundamental part of postoperative care, often extending for up to five years post-surgery. Depending on individual circumstances, additional therapies such as chemotherapy or radiation may be needed, underscoring the multifaceted approach to cancer care.
Transoral robotic surgery is not just a passing trend; it symbolizes a transformative period in surgical standards and practices. By integrating cutting-edge technology into clinical frameworks, TORS offers a promising avenue for enhancing patient outcomes in the realm of head and neck surgery. Its ability to minimize recovery times, reduce complications, and improve precision establishes it as an exceptional option for many patients facing complex surgical challenges.
Ultimately, as patient needs continue to evolve, so too must surgical approaches. TORS exemplifies a commitment to innovative healthcare solutions, placing emphasis on both efficacy and quality of life. As more healthcare facilities adopt this surgical modality, it is crucial for patients to remain informed and engaged in discussions with their healthcare providers regarding the optimal treatment options available to them. As the field grows, so will the opportunities for breakthrough discoveries and improved therapeutic strategies.